Maintenance optimisation for multi-component asset with fault propagation
Overview
Complex industrial assets such as power transformers are subject to accelerated deterioration when one of its constituent component malfunctions, affecting the condition of other components – a phenomenon called ‘fault propagation’. Zhenglin’s research is to design a novel approach for optimizing condition-based maintenance policies for such assets by modelling their deterioration as a multiple dependent deterioration path process. The aim of the policy is to replace the malfunctioned component and mitigate accelerated deterioration at minimal impact to the business. The maintenance model provides guidance on determining inspection and maintenance strategies to optimize asset availability and operational cost.
Aim
To present a novel condition-based maintenance policies for multi-component asset with fault propagation and to improve the performance of multi-component asset by mitigating the risk of fault propagation.
Methodology
- The methodology is mainly based on mathematical modelling.
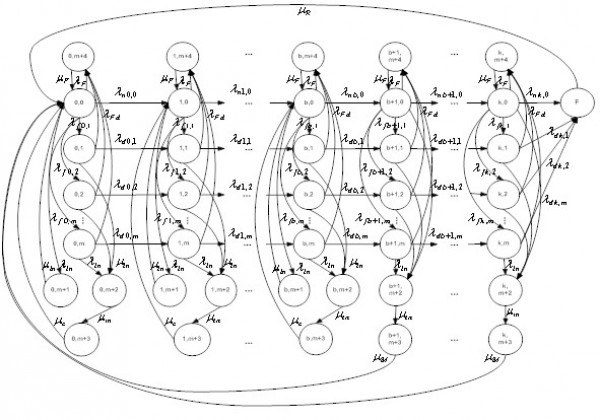
- A vector-valued continuous-time Markov chain to formulate the deterioration process of multi-component asset was implemented.
- The deterioration model is then simplified by continuous-time Markov aggregation. Maintenance strategy is optimized by multi-objective dominance based simulated annealing.
- The result is verified by extreme scenarios and validated by case study of high-voltage power transformer.
Novelty & Contribution
- It captures the phenomenon of fault propagation and brings the model closer to reality.
- it overcomes the state space explosion dilemma and attains mathematical tractability.
- it mitigates the propagation and improves the performance of condition based maintenance.
Supervisor









