Intelligent Logistics - Ongoing Projects
Shoestring Logistics
The Shoestring Logistics project is a part of the broader Shoestring Manufacturing project hosted at DIAL. Shoestring Logistics aims at, first, identifying the requirements of the small and medium logistics enterprises in the UK by conducting industrial workshops, and second, developing solutions towards these requirements using off-the-shelf solutions that are accessible to the participating companies.
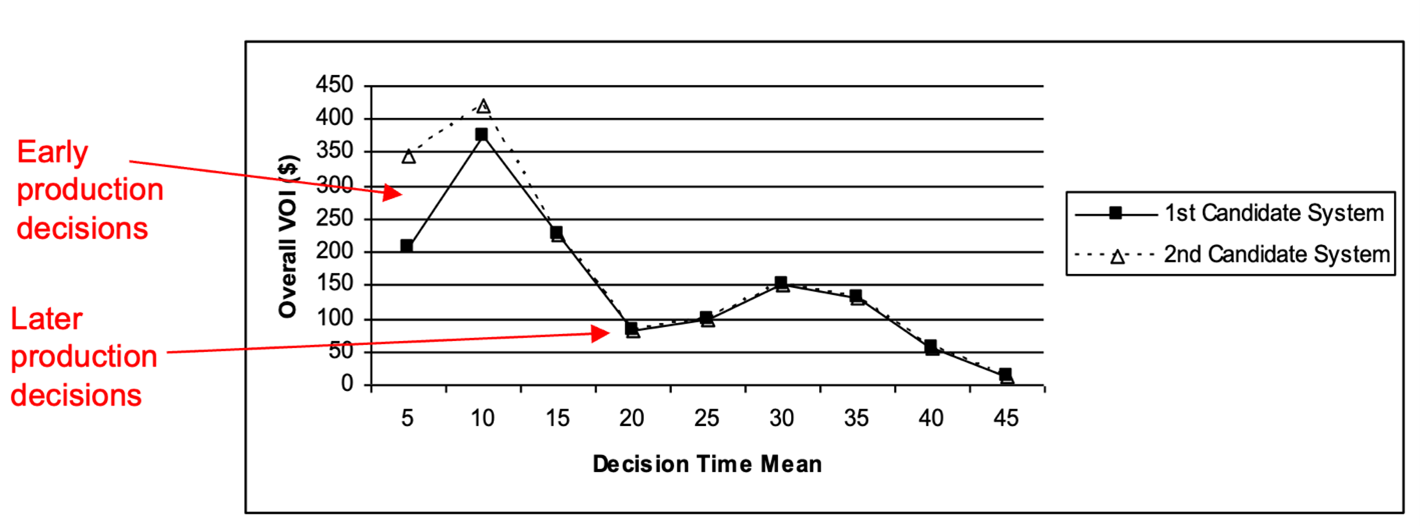
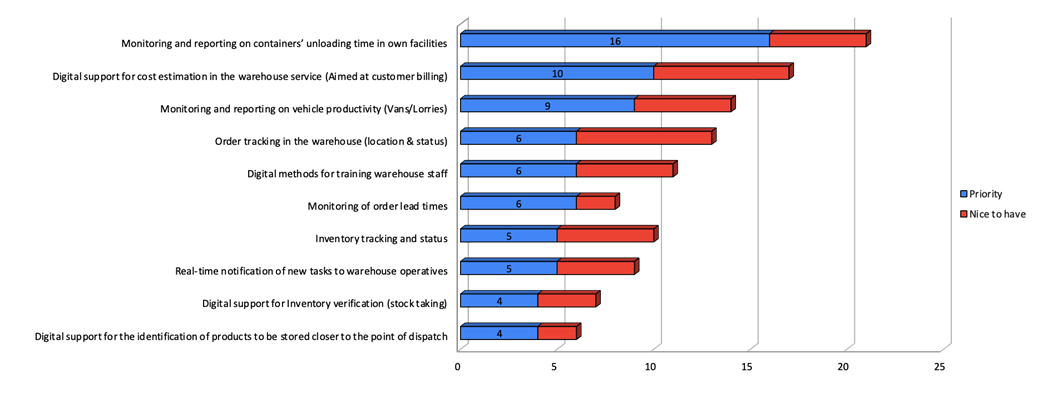 Fig. Needs of the UK logistics SMEs identified through Shoestring Logistics workshops
Fig. Needs of the UK logistics SMEs identified through Shoestring Logistics workshops
- Asset utilisation monitoring with Amco Logistics
Monitoring the usage of warehouse logistics equipment was identified as one of the top requirements through the Shoestring Logistics workshops. To that end, a very narrow aisle vehicles (VNAs) usage monitoring solution is developed, and a pilot is implemented in collaboration with Amco, a UK-based logistics company. By monitoring the vibration signals and using a classifier algorithm, this pilot can quantify the usage of the VNAs rented by Amco. A user-friendly interface is also included in this pilot.
Fig. VNA utilisation monitoring Shoestring solution - Meachers Global Logistics Ltd
In collaboration with Meachers Global, another UK-based logistics company, a Shoestring solution to monitor and display the time and number of people involved in the unloading of each container type is developed. This data is key for making commercial decisions while loading/ unloading delivery trucks. - Other Shoestring Logistics solutions
Apart from these solutions, several other Shoestring solutions such as OEE measurement and monitoring, push-button reorder system, etc. are developed in collaborations with logistics companies across the UK.
Intelligent Products: Enabling Customer Oriented Logistics
- Challenge
i. Evaluating benefits for customer / provider of making product intelligent.
ii. Allowing order to (automatically) add priority after delivery process has begun. - Approach
i. Game theoretic model for evaluating tradeoffs in late decisions.
ii. Likelihood of disruptions and effectiveness of planning impact benefits.
Value of Logistics Information
- Challenge:
i. improved visibility of incoming shipments
ii. select between two possible tracking system configurations - Approach:
i. Establish improved information quality owing to additional measurements
ii. Model impact of improvement on production decisions
iii. Other applications in reordering, OTF
RedBite Solutions (IfM spin out)
- Automated asset tracking made simple
- Powering the world’s largest RFID deployment
Achieving Leveraged Advantage from Distributed Information
(ALADIN)
- Challenges
i. Vast volumes of data from the global supply chain all flowing into OEM.
ii. Sub-Tier Suppliers: Roughly 20:1 ratio
iii. Data stored in many information systems (silos)
iv. 100s of Supplier Management & Procurement Systems
v. The sheer volume of data creates missed opportunities for users - Approach
i. Transform data from passive to active, with organic awareness of its own value
ii. Data autonomously seeks systems of value
iii. Autonomous delivery to users that will realize the greatest benefit from the data - Benefits
i. Reduce non-value-added data work
ii. Increase exposure to valuable data
iii. remove burden of processing/storing non-valuable data
iv. Reveal opportunities that would not be realized by the user
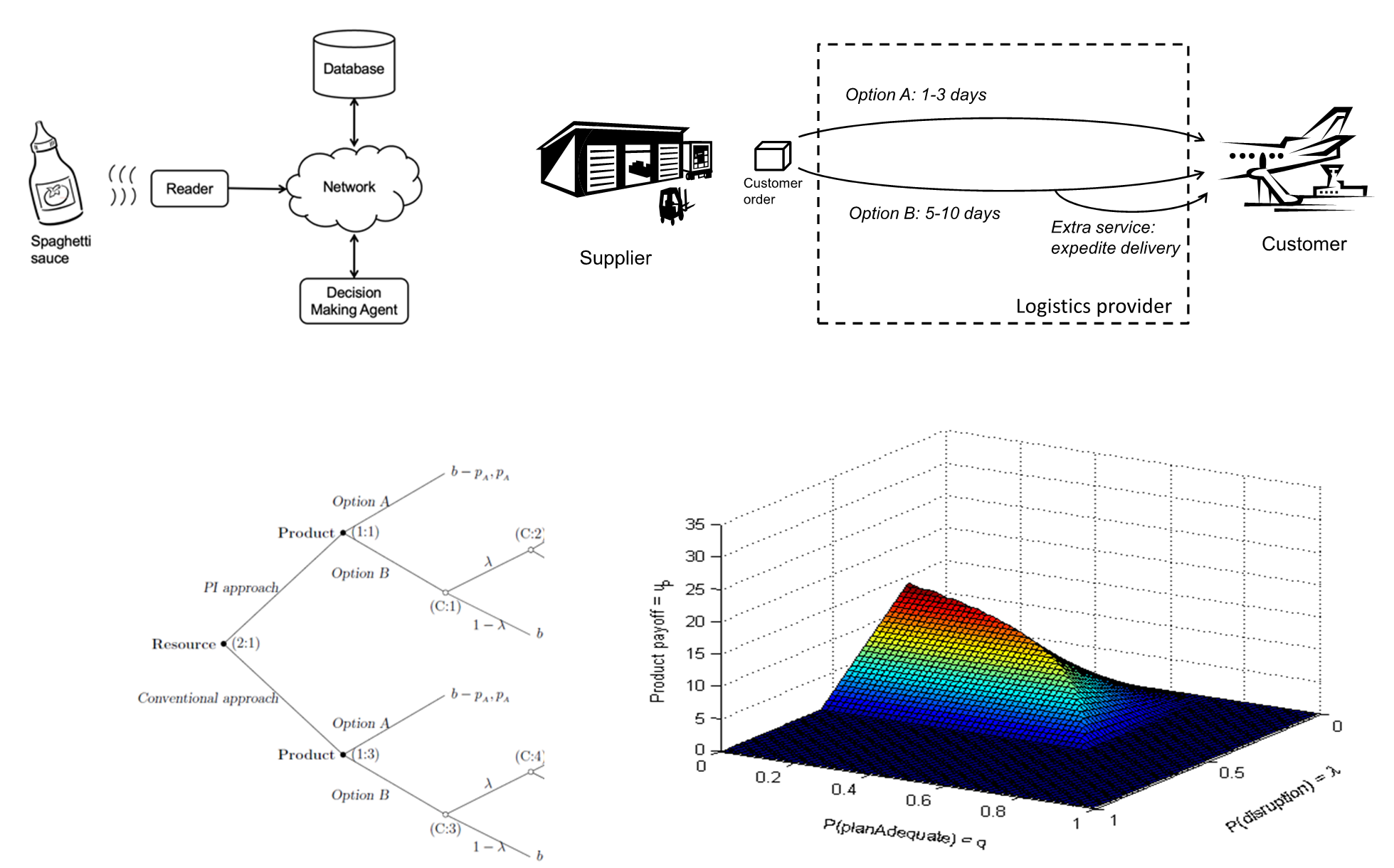
5G and IoT-enabled Digital Twins For Dockside Logistics
- Challenge:
i. Anomaly detection with poor quality monitoring data from multi-modal IoT sensors - Approach:
i. Unsupervised discord detection
ii. Combination of condition monitoring and operational data - Benefits:
i. Works in the absence of labelled data
ii. Interpretable in combination with operational data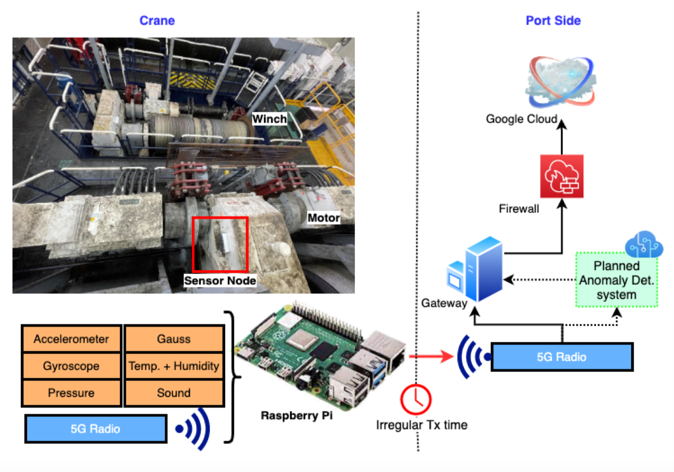
IT Architectures for Logistics Integration
- Aim:
To investigate how existing logistics-related information systems must evolve to address future logistics needs. - Challenges:
i. Mismatches between operations and data
ii. Difficulty in offering integrated logistic services to clients.
iii. Dealing with differing B2C and B2B commerce requirements. - Approach:
i. New concept: Indefinite Information System to help avoid disruptions caused by data mismatches.
ii. Develop a flexible and robust order management system for improved inventory management
iii. Develop a framework for what needs to be employed in terms of IT systems and operations in logistics to support B2C-like commerce.
Airlines Performance and Disruption Management
- Aim:
To investigate the ways which flight disruptions & delays impact on in day schedules and airline performance - Challenges:
i. Understanding the propagation of delays
ii. Developing an approach for recovering schedule with minimum impact (in day)
Dynamic and Adaptive Supply Chain Logistics Sponsored by Y H Global
- Aim:
To improve and stabilise the performance of warehouse and logistics operations in e-commerce - Approach:
i. Management of warehouse operations to deal with disruptions
ii. Coordination of warehouse and transportation processes
Data Integration Platform for the Supply Chain
- Aim:
To investigate the benefits of data sharing on logistics across the supply network - Approach:
Mapping, modelling and demonstration of data sharing opportunities 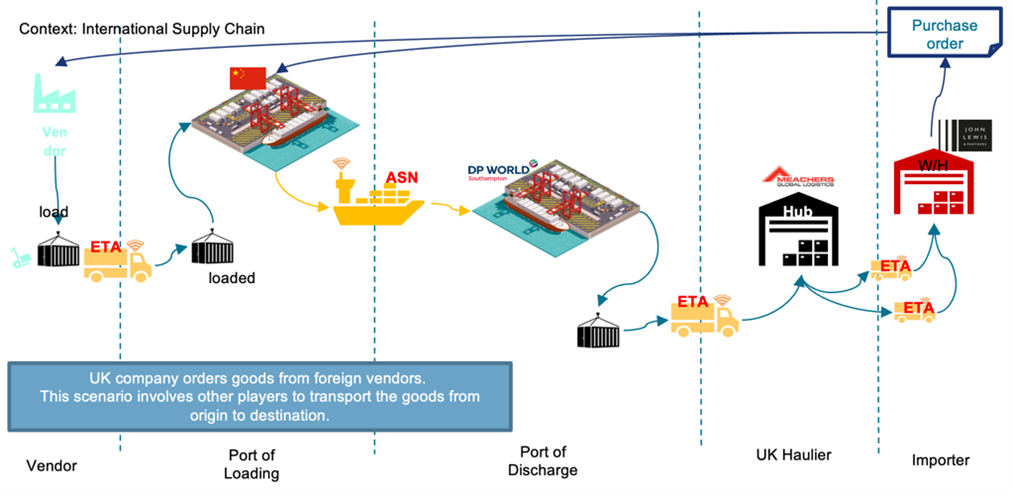
Big Data to Enhance Supply Chain Operations
- Project Aim:
To develop a system to make predictive interpretations about potential supplier operational non-performance. - Challenges for manufacturers:
i. Parts shortages, for a variety of reasons:
ii. suppliers being overloaded by orders from other customers,
iii. day-to-day delays during transportation of goods,
iv. suppliers not being able to satisfy manufacturing demand, these can result in significant production delays. - Approach:
i. The Virtual Intelligent Production, Procurement and Prediction (VIPr) project aims to address these issues by:
ii. Using public data to model the supply chain
iii. Utilising data analytics to make predictive interpretations about potential supplier operational disruptions.
Other Industrial Projects
- Scania Spare Parts Ltd
This project is in collaboration with Scania, a Swedish truck-manufacturing company, that aims towards forecasting the monthly spare-parts requirements using collaborative learning techniques. The challenge arises due to many spare-parts which are often critical and therefore there exists limited historical training data. Moreover, Scania manufactures a diverse range of trucks, requiring a diverse set of spare-parts. This constitutes a network of spare-part dependencies.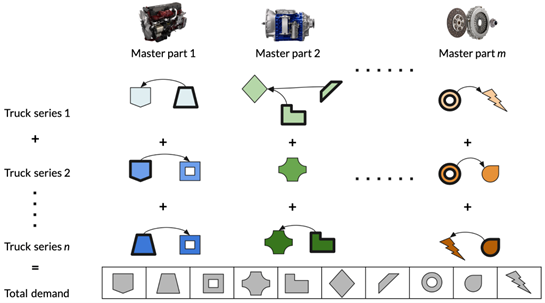
Fig. An example of spare-parts interdependencies
- Delivery Hero
i. Customer demand forecasting
This project aims at forecasting customer demands for the European urban logistics company Delivery Hero, through component-wise statistical hierarchical models. This addresses a common cold-start problem often faced by companies operating in this sector while predicting customer orders, a critical challenge in overall operations planning.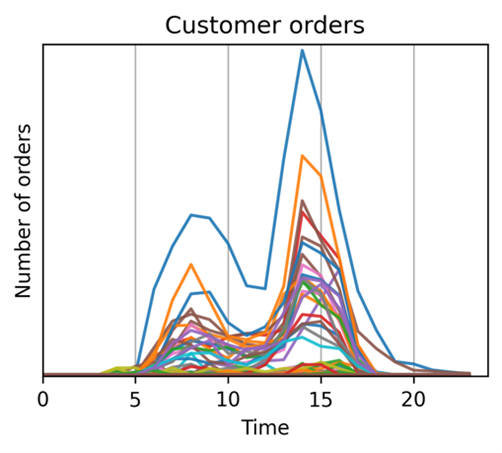 Fig. An example of wide range of customer orders, each colour representing a different city
Fig. An example of wide range of customer orders, each colour representing a different city
ii. Quantifying performance indicators for urban logistics
This is an MET Masters project of Kuba Ciukiewicz from 2023, that aims at developing the key performance indices (KPIs) for Delivery Hero. These KPIs make sure an optimal balance is maintained between customer, courier, and business satisfaction. This project won the best project award in the year 2023.
iii. Q-commerce product recommendation engines
There are two MET Masters projects of Linda Chen and Ioan Webber, from 2024 that aim at recommending substitutions for grocery products. This is critical for companies operating in the quick-commerce sector.
Two techniques are proposed via the projects, (1) involving probabilistic association rules and (2) contextual multi-armed bandits, towards addressing the aforementioned industrial problem. - Hivebound.io
This is a project in collaboration with a London-based startup that aims at optimising multi-party supply chain logistics.
Past Projects:
a. AutoID Centre/ RFID
b. IT Architectures for Logistics Integration (ITALI)
c. Dynamic and Adaptable Supply Chain Logistics System (DASHLog)
d. Building Radio Frequency Identification for the Global Environment (BRIDGE)