Contextual inquiry
A specific name for a style of user interview, conducted within the context of the customer's activities. This approach enables combines the benefits of observational approaches and the standard face-to-face interview. It is intended to be an interactive exploration of the issues, hence the reason for being called inquiry rather than interview.
The main difference between the contextual inquiry and the traditional interview is that the inquiry demands a partnership between customer and product development team. The product developers bring special product knowledge, and the customers bring special knowledge about his or her job or specific needs. Both can be viewed for experts and the inquiry is a joint search for information.
General approach
Planning and preparation
As with traditional interviewing, the meeting needs to be prepared. The interviewees need to be identified and the activities of the session must be planned. Unlike the interview, which may take place in the meeting room however, this approach demands that the discussion is held in the normal environment of product use.
Stage setting
Essential, to ensure that the customer understands the goals of the contextual inquiry and is comfortable with the overall process.
Context - observe the product in use
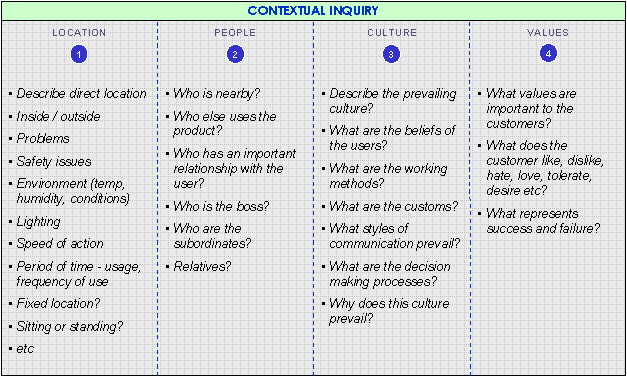
Before structured questioning, the team should aim to understand the context of use. This could be achieved in a number of ways, including demonstration, observation or shadowing. Issues of concern relate to the location, people, culture and values. These are described in more detail in the illustration opposite. If appropriate, draw a flow diagram of activity and collect any physical outputs.
Summarise and share
Summarise your observations and share any conclusions with the customer. Show flow diagrams and seek clarification or correction where appropriate.
Semi-structured questions
General questions to gain a broad understanding of the views of the experts relating to the problem. Responses should be collated and summarised.
For more information, please contact:
T: +44 1223 764830









